Reversible Dye Termination Sequencing by Synthesis Technology
The first Illumina NextGen sequencing platform, the Genome Analyzer (developed by Solexa), was launched in 2006. Illumina’s reversible dye termination sequencing by synthesis technology is the foundation for their NextGen instruments: HiSeq 2500/3000/4000, MiSeq, NextSeq 500, MiniSeq and the HiSeq X10/x5 series.
The basic principle behind how Illumina sequencing works is fluorophore detection. First, libraries undergo bridge amplification to generate clonal clusters of library molecules directly on the surface of the sequencing flow cell. The nucleotides used during sequencing are labeled with a different fluorophore and are all chain terminating. However, their chain terminating properties are reversible. During sequencing, all nucleotides are pushed through the flow cell lanes and allowed to anneal to the library clusters, with only one nucleotide annealing at a time. After annealing, the excess nucleotides are washed away and the fluorophore emissions from each cluster are imaged. An enzymatic reaction will cleave off the fluorophore and the next round of nucleotide annealing will take place. Each nucleotide is coded by a different color emission and the resulting data is converted by the software into nucleotide sequence.
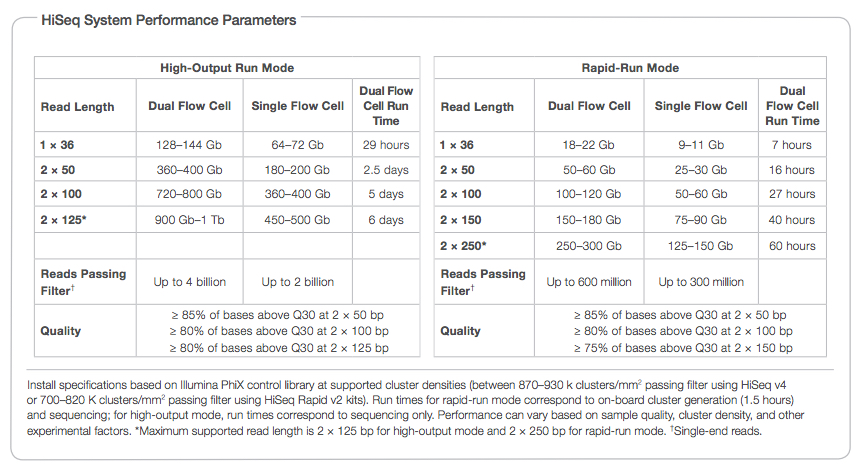
HiSeq 2500 Platform Specifications
UCONN Researchers have access to HiSeq 2500 sequencing through two vendors – New York Genome Center and Macrogen (Special pricing available). HiSeq 2500 specifications can be found in the table below (from Illumina Sequencing Specification sheet; full document can be accessed here).
- To get an estimate of sequencing coverage for your experiment, use the web-based calculator found on the Illumina Website
Become a member of myIllumina to get access to assay design tools, product updates and more!
Illumina Sequencing Applications
There are several supported applications for Illumina DNA, RNA and epigenetics sequencing. Click the links below to get more information on their most popular applications.
- Whole Genome Sequencing
- Targeted Resequencing
- de novo sequencing
- RNA-Sequencing applications such as mRNA-Seq, Total RNA-Seq, small RNA-Seq and Ribosomal Profiling,
- ChIP-Seq
- Methyl-Seq